GBRUnionwas developed to help designers clean and convert Gerber files into contour data. It does this by performing a union operation on draws, flashes and areas. Once a layer has been unionized there are no overlapping or touching boundaries. The resulting file can be output as Gerber, DXF, GDSII or EGS Archive.
One of the most common uses of GBRUnion is by designers working with EM field simulation software. These designers need to take layout data from PCB design tools and import it into their simulator. GBRUnion cleans the data, allows extraction of a small window and exports Gerber into a variety of formats.
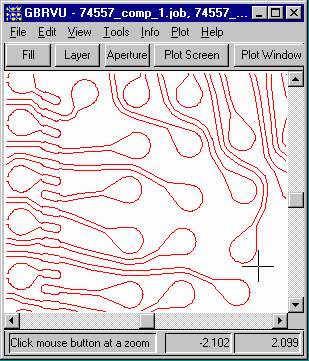
At right is a snapshot of Gerber data for the top metal layer of a ball grid array. You cannot easily tell what Gerber commands (strokes and flashes) are used to create the image when it is displayed "solid".
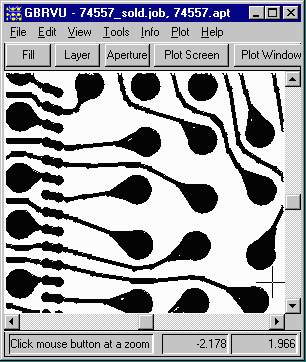
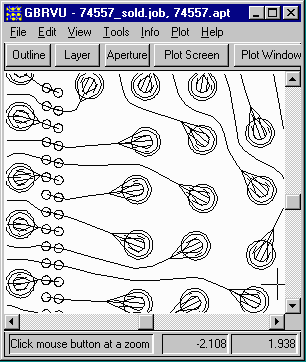
If we change the viewer to display only center lines we can now see that the Gerber file consists of many overlapping strokes and flashes. If you were to import this directly into a EM simulator, one would have quite a lot of cleanup to do before the data was ready for analysis.
Running this file through GBRUnion reduces the geometry to simple and clean contours. This is how a field analysis tool would like to read the data so that it can be efficiently "meshed."
Several outputs are available depending on the tool you use: DXF (Ansoft/Maxwell), EGS ( for users of Agilent's ADS/Momentum) or GDSII. There is also a version of GBRUNion integrated into CST's Microwave Studio.