GDS Compact reduces the complexity of stream files by performing a unionization on a cell by cell basis - thus removing any superfluous and redundant polygons that do not contribute to the mask output but which may slow down DRC, LVS and OPC tools. It does not effect the file's hierarchy of cells.
Many designs are built by synthesis tools and these tools often leave additional polygons that are "covered" by other polygons and do not in any way contribute to the final appearance of the mask. These "redundant" polys may affect post tapeout tools such as DRC engines, LVS engines and OPC or RET engines.
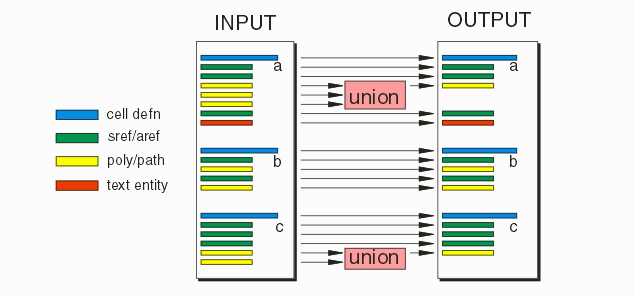
A GDSII file is a collection of cell definitions. Within each cell there are really only three interesting record types: polygons or paths (lumped together because they are geometries; SREF/AREF which are references or instances of cells; and text entities which are not used for the mask but are often used for purposes of DRC and LVS.
What GDS_COMPACT does, on a cell by cell basis, is:
unionizes all overlapping or touching geometries
Passes all SREFs or AREFs directly to the output without change.
Passes text entities directly to the output without any change
Each layer in the input is treated independently.
Example
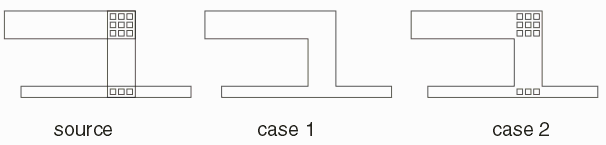
The source data (a single layer) consists of three paths carrying power and two arrays of vias.
Case 1 - the paths and the vias all are members of the same cell. After the union operation the output file will have a single polygon.
Case 2 - the paths belong to one cell and the vias are placed using AREFs. After the union operation the paths have been unionized but the vias are not affected as unionization does not occur outside of the cell.
