This page describes the basic procedure for translating a DXF file to GDSII using ASM 3500 on Linux.
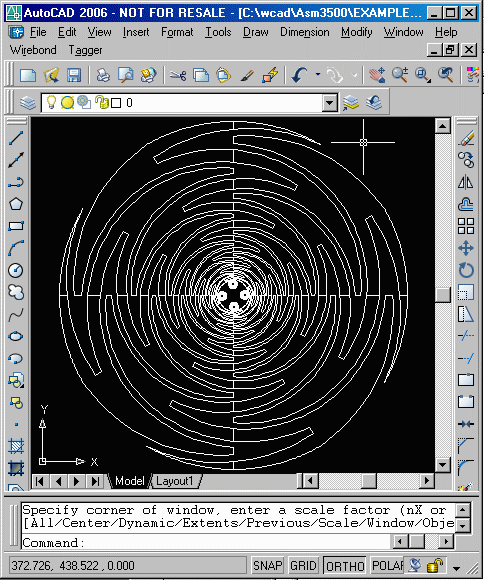
Before translating the file, one must know a few things about the DXF file - Most importantly, the units of the DXF file. In this example, we will use one of the DXF files in our examples directory called sinuous.dxf - The file is in units of mils.
In the example at right, all polygons are drawn on one layer and they are all drawn as zero width closed polylines. Our translator also supports drawing polygons as lines and arcs as long as they are connected end to end.
Start xdxf2gds64 and open the file you wish to convert to GDSII: sinuous.dxf.
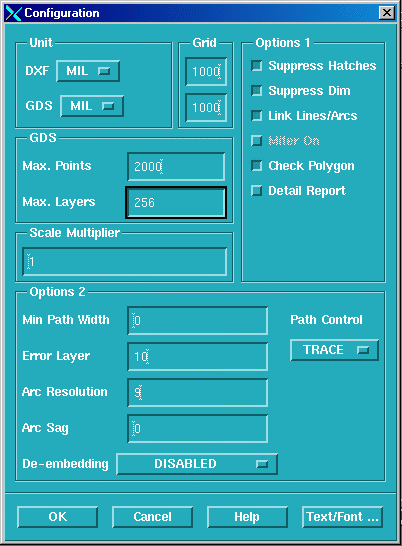
From the main menu, click on the Configuration button to open the dialog and select the Translator tab. Set the proper units and grid which in this example is units of mils, and grid of 10000.
Set the Max Points to 2000.
Set the Error Layer to 10 - any open polygons will go to that layer.
Set the Arc Resolution to 9 degrees.
From the Main Menu, Click on the Layers button. The Layer Table will appear. Make sure that the layer(s) you wish to translate have been selected with a checkmark next to their layer name.
In this example, the polygons were all drawn on layer "0" so that is the only layer we need to convert.
Click OK to close the Layer Table.
Start the Translation from the Main Menu by Clicking on the Translate button.
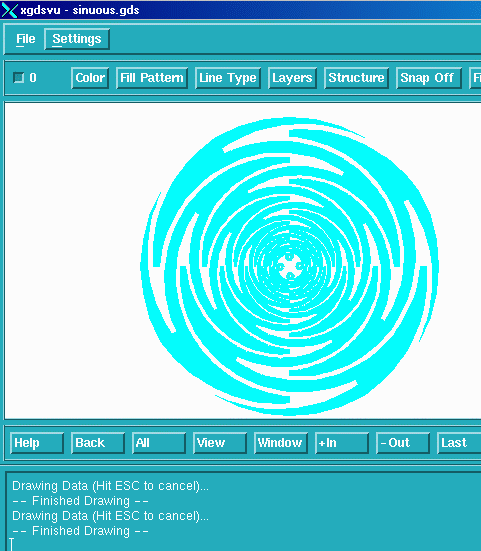
Click on the View GDSII button from the Main Menu to view the resulting GDSII file.
Idealy, you want all polygons to be filled. If there are any open polygons in the DXF file, they will go to the layer we defined as the error layer in the Configuration menu.