Installing the LSERV License Manager on NT
General Requirements
|
Instead of the hardware key, lserv locks to the NT machine’s hostid which is derived from the network card's MAC address. You must have TCP/IP services configured correctly on both the license server machine and on all client machines. Clients can be either Windows 95 or NT
but the license manager runs only on NT
|
Installing the LM on a NT Server
Log on to Windows NT as a user with administrative rights: either as root or administrator. Run setup.exe either from the lservnt diskette or the cd directory /lservnt/setup.exe.
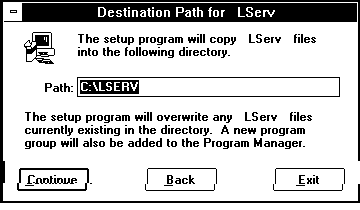
Select the directory where lserv is to be installed; the default directory is c:\lserv. Only about 350k bytes are required.
|
|
The following files are installed in this directory:
lserv.exe the licensing daemon
lserv.dll DLL used by lserv.exe
loadls.exe utility to load lserv.exe into “system services”
loadls.ico icon file of loadls.exe
echoid.exe returns the hostid/hostname
echoid.ico icon file of echoid.exe
lsmon.exe displays active lserv daemon and licensed programs
lswhere.exe searches network for active lserv
Adding LSERV to System Services
At the end of the installation, you will be prompted to “ADD” LSERV to the system “Services”.
Adding or loading lserv does not automatically start up the daemon itself. The next section discusses how to obtain your machine’s hostid, keystrings and start up the license manager.

|
Getting Your Machine’s Hostid
|
After the installation is finished, a group called “LicenseServ for Windows NT” will be created;
one of the utilities in this group is called "EchoID". Double click on the EchoID icon to obtain your machine’s hostid, hostname and IP address.
|

|

|
Either email or fax the Hostname and Hostid information to Artwork in order for us to generate license keys.
Note: You can also obtain the MAC address directory (from which the hostid is derived) by typing:
nbtstat -a hostname
This is useful to know if you are trying to get your keycodes in advance of obtaining the lserv software.
|
Creating the LSERVRC File
Once you have received your keystrings use notepad or other editor to create a file called
\WINNT35\SYSTEM32\LSERVRC
Enter the keystrings you obtained form Artwork into this file. Make sure that the file is really saved as LSERVRC. Sometimes your text editor will force a suffix such as .txt and you may have to rename the file manually.
|
Starting Up LSERVE the First Time
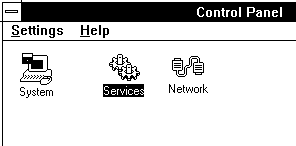
Go to the Control Panel and double click on the Services icon.
|
|
|
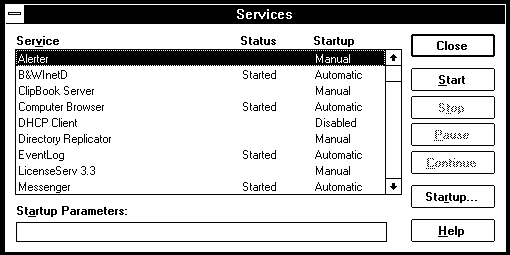
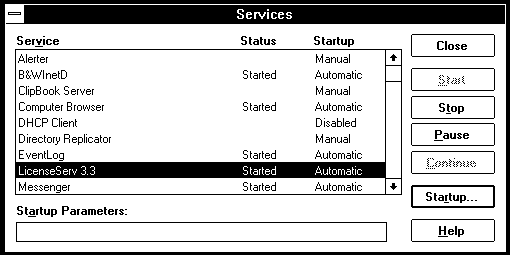
A list of installed services will appear; select LicenseServ 3.3,then click Start.
|
|
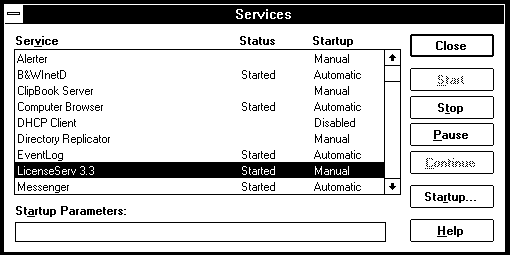
You will see the status of Licenserve 3.3 change to Started.
|
|
Starting LSERV Automatically on Boot Up
By default the lserv service uses "Manual" startup. Each time the server reboots you must manually restart lserv from the Services menu. This is probably not your desired behavior.
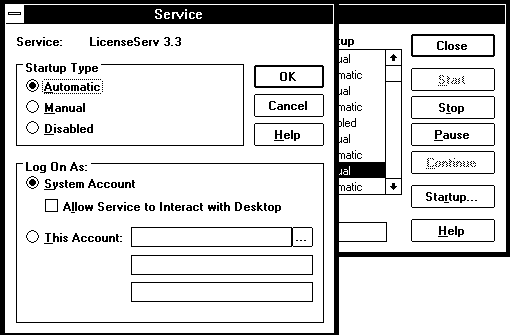
To make lserv start up automatically after a reboot, click the Startup button from the Services menu.
A new windows will pop open. Click the Automatic radio button; then click the OK.
|
|
Back in the Services window, LicenseServ 3.3 will have changed from Manual startup to Automatic startup; click on the Close button to close the window. Now each time that the NT server is rebooted the lserv daemon will start automatically
|
Set LSHOST Environment Variable
|
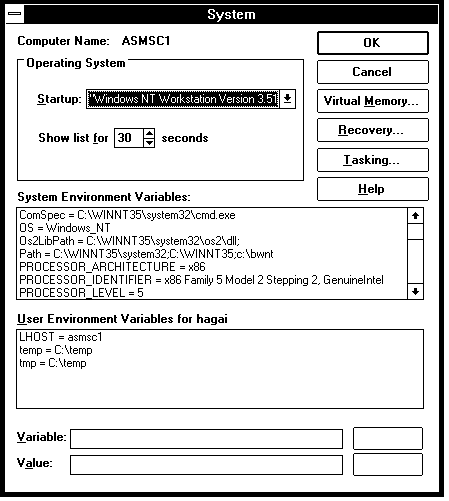
Create an environment variable called LSHOST and set it equal to your hostname. The echoid program returns the hostname, or you can use the command: hostname
From the Control Panel double click on the System icon.
In the field labeled Variable type: LSHOST
In the field labeled Value Type: hostname
Click on the Set button
You will see the new entry appear as a User Environment Variable.
|
|
Name Resolution Problem?
Some NT machines do not have the name resolution correctly set up. How can you tell? If you cannot ping your own machine using its hostname, then the name resolution is broken. Check the following file:
/WINNT35/SYSTEM32/DRIVERS/ETC/HOSTS
You should see the IP address vs host name for the various machines attached to your network. Check to make sure that your own machine is listed. For example on one of our
internal machines (asmsc1) we have the entry:
205.179.74.1 asmsc1 ASMSC1
|
Testing Lserv
You should verify that your keystring is entered correctly by using the lsmon utility to display the status of lserv. Because this is a command line based program you must first open a DOS box in NT and then type:
c:\lserv\lsmon.exe
Lsmon will return a list of licensed features. Each feature represents an application program or a module of an application program. Unfortunately the feature name used by lserv may not always be the same as the program name. For example the feature name for GDSPLOT is ACS3520.
|
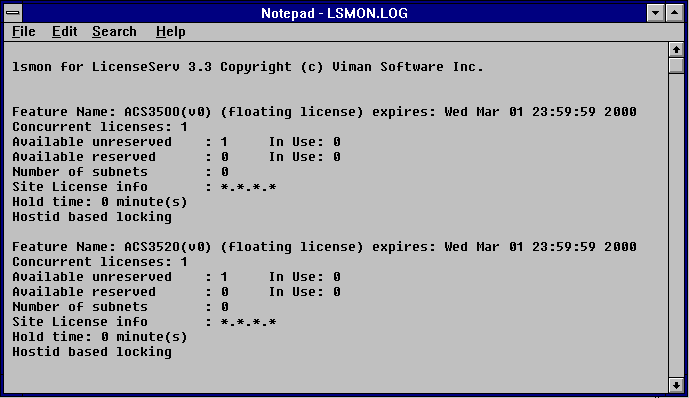
If lsmon does not return a licensed feature several things may potentially be wrong:
- Incorrect code string or missing LSERVRC file
- LSHOST environment variable not set or set incorrectly
- Name resolution not working
|
Keying the Applications
When you install the application you must configure it to get a license from the license server. This is done by giving it special keycodes. When prompted to enter keycodes for the application do not enter the lserv codes. Enter the codes:
NETWORK NETWORK NETWORK NETWORK NETWORK NETWORK NETWORK as shown:
|
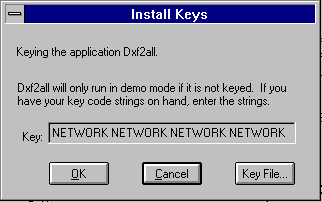
|
Changing the LSERVRC License Strings
If for some reason you need to edit the LSERVC file, either to add a new program or to correct an error in the string, you must stop and restart lserv from the Services menu. Lserv only reads the LSERVRC file when it starts up.
Typical Problems
1. The license string in LSERVRC may be wrong. Verify carefully that it is correct. If you need to edit the string make sure to stop and restart Lserv from the Services Window.
2. The lserv Daemon may not be running at all. Verify that it is running from the services window. Under the status column it should say "Started".
3. The LSHOST environment variable may not be set for the particular user or machine.
4. The TCP/IP may not be configured on the particular client machine.
5. The application may not have the special NETWORK NETWORK NETWORK.... key codes.
6. Name services may be messed up. Make sure you can ping the license server machine from each and every clint.
|











