File Size Issues in AutoCAD
Sometimes large GDSII files when translated to DXF and loaded into AutoCAD, will cause the program to crash or stop responding. AutoCAD is not only known for having a hard time displaying large files, but often smaller files with lots of arrayed data will be exploded in AutoCAD, increasing the file size internally and causing the program to crash.
The following example will show a sample GDSII file (test12.gds), which is 11.34 MB in size. When translated to DXF the file size grew to 29.5 MB. After loading this file into AutoCAD, the program stopped responding after about a minute due to the large amount of data contained within it.
First, lets take a look at the sample GDSII file in Artwork's QCKVU and try to determine the best way to reduce the file size without losing any pertinent data.
The Problem
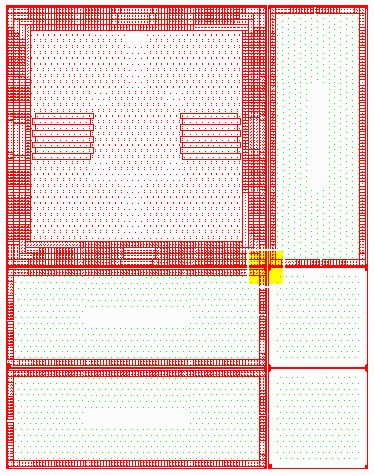
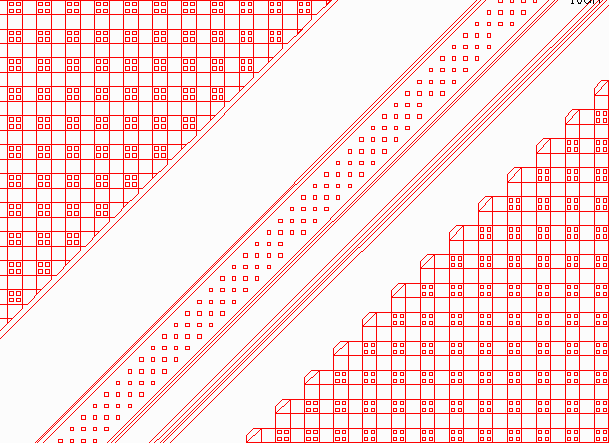
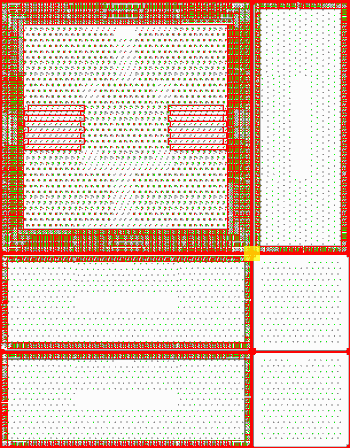
This is a full view of our sample file in QCKVU. Obviously, it's not possible to determine why the file is so large from this view. So, we'll take a closer look at a more specific area of the drawing (highlighted in yellow). Basically what we're looking for are dense areas which contain lots of blocks.
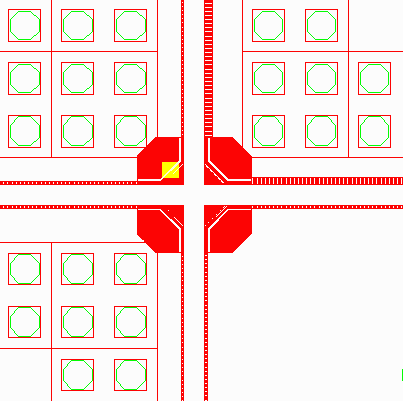
At left is a zoomed view of the highlighted window from the display shown above. Notice the large red areas in the center. These appear to be very dense. We'll zoom in even further, (highlighted in yellow), to examine this section in greater detail.